Online Help
Document Types Options
An Overview of Document Types
This page allows you to define document types and specify special options for document types. There are three types of document types in ExamDiff Pro:
-
 Default/Plain Text
is the default document type that is assigned to all files
that do not match any other document types. This document type cannot be deleted or renamed, and
cannot participate in syntax highlighting and comment ignoring.
Default/Plain Text
is the default document type that is assigned to all files
that do not match any other document types. This document type cannot be deleted or renamed, and
cannot participate in syntax highlighting and comment ignoring.
-
 System types are
those types that come preinstalled with ExamDiff Pro. They cannot
be deleted or renamed, but can be assigned to different file extensions. These document
types can participate in syntax highlighting and comment ignoring.
System types are
those types that come preinstalled with ExamDiff Pro. They cannot
be deleted or renamed, but can be assigned to different file extensions. These document
types can participate in syntax highlighting and comment ignoring.
-
 Custom types are
those types that are user-created. They are the only types that
can be deleted and renamed. These document types can participate in comment ignoring,
but cannot participate in syntax highlighting.
Custom types are
those types that are user-created. They are the only types that
can be deleted and renamed. These document types can participate in comment ignoring,
but cannot participate in syntax highlighting.
Dialog Box Options
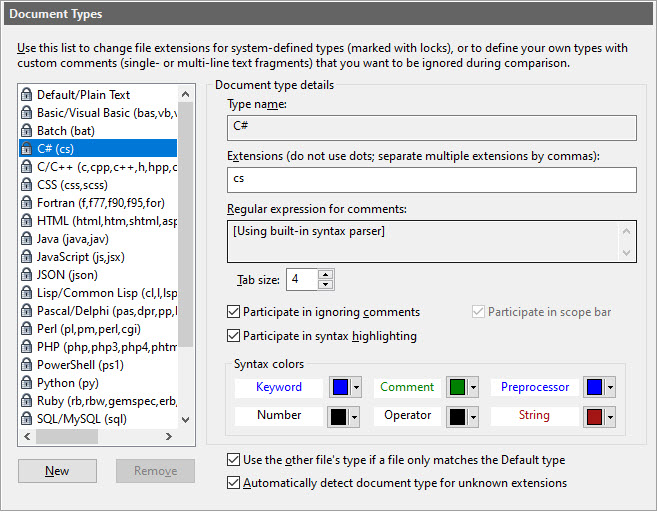
List of document typesContains a list of all document types, and corresponding file extensions.
New
Creates a new blank document type.
Remove
Deletes the selected document type. Only user-created types can be deleted.
Document type details
Contains options specific to each document type:
-
Type name
The name of the document type. Only user-created types can be renamed.
-
Supported features
A list of type-specific features supported for this document type. Supported features include:
- basic syntax highlighting: highlights basic syntax elements like keywords and comments
- advanced syntax highlighting: parses the file fully and highlights all relevant syntax elements
- scope bar: support for displaying a scope bar
- comments: support for ignoring comments (either defined by the syntax parser for built-in types or defined by a custom user-provided regular expression)
-
Extensions
File extensions that the document type applies to.
-
Tab size
Sets the tab size (that is, the number of spaces in a tab) for the document type. This option only takes effect if Use document type settings is enabled.
-
Enable syntax highlighting (built-in types only)
Highlights certain syntax elements during comparison. Diff highlighting takes precedence over syntax highlighting, so syntax highlighting only takes effect on identical blocks. The colors used in syntax highlighting can be modified in the Display | Syntax Colors Options panel.
-
Use syntax parser to detect comments (built-in types only)
Use the built-in syntax parser for this document type to identify comments, that will be ignored if the Ignore Comments comparison option is enabled.
-
Regular expression for comments (custom types only)
The regular expression (if any) that defines comments for the document type. This option can only be set for custom types; system types use the same parsing algorithms that are utilized by syntax highlighting. Note that we use the term "comments" in a very broad sense; any single- or multi-line part of a text file can be considered a "comment" as long as it is defined by a regular expression.
-
Single line comments
Single line comments (such as // in C++), use the following regular expression: [comment symbol].*?\n . For example, the regular expression for C++ style comments is //.*?\n . Note the non-greedy ? operator.
-
Multi-line comments
Multi-line comments (such as /* */ in C), use the following regular expression: [start comment symbol].*?[end comment symbol] . For example, the regular expression for C-style comments is /\*.*?\*/ . Again, note the non-greedy ? operator.
-
Combining comments
Different kinds of comments can be combined ("OR-ed") using the | character. For example, the regular expression /\*.*?\*/|//.*?\n ignores both C and C++ style comments.
-
Single line comments
If this option is selected and two files are compared, one of which matches a document
type and the other only matches the Default type, then both files will be treated as though
they match the document type. This is useful for source control, because source control
file versions often have extensions different from the actual source files.
Automatically detect document type for unknown extensions
If this option is selected, ExamDiff Pro will automatically detect document types (using the
Guesslang open-source machine learning library)
in situations where the document type of a file being compared is not otherwise known. If the type of a file
still can't be detected, or the detected file type doesn't match any document type that ExamDiff Pro supports,
the file will be treated as having the Default/Plain Text type. For auto-detected files, matching
plug-ins will be executed.
Document type auto-detection will happen in any of the following situations:
Document type auto-detection will happen in any of the following situations:
- a file is compared either without a extension or with an extension that doesn't correspond to any known ExamDiff Pro document type
- a comparison is initiated from clipboard contents
- text is pasted into a comparison window from the clipboard
Copyright © 1997-2025 PrestoSoft LLC. All rights reserved.
